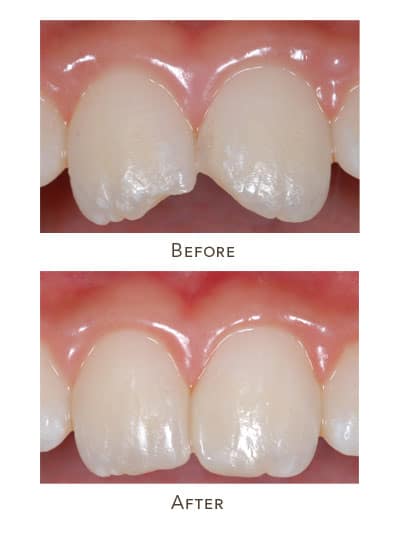
Dental bonding is a fast, conservative way to repair small chips, close minor gaps, smooth uneven edges, or improve tooth shape. We use a tooth-colored composite resin, shape it right on the tooth, and harden it with a curing light—then polish it so it blends in naturally.
Bonding is often a great choice when you want a meaningful improvement without changing your whole smile.
How Long Does Bonding Last?
Bonding can last for years, but it depends on where it is, how you bite, and your habits (like nail biting or chewing ice). It may wear faster on edges that take a lot of force. We’ll tell you what to expect for your specific case and how to keep it looking good.
Bonding vs. Veneers
Bonding and veneers can both improve appearance, but they’re used for different situations.
Bonding can be ideal for:
- Small chips or cracks
- One-to-two teeth that need cosmetic improvement
- A “test drive” before a bigger veneer case
Porcelain veneers may be better when:
- You want a broader smile makeover (4–10 teeth)
- You want stronger stain resistance
- You want the most durable, long-term cosmetic result
- We’ll help you choose the option that makes sense for your goals—and for your tooth structure.



